Intel Arc is a graphics processing unit (GPU) designed by Intel. Intel Arc is competing with Nvidia’s GeForce and AMD’s Radeon lines.
The first generation of Intel Arc GPUs (codenamed “Alchemist”) was released on March 30, 2022. It will come in both add-on desktop card and laptop form factors. TSMC manufactures the die, using their N6 process. Alchemist uses the Intel Xe GPU architecture, or more specifically, the Xe-HPG variant. Alchemist supports hardware-based ray tracing, XeSS or supersampling based on neural networks (similar to Nvidia’s DLSS), and DirectX 12 Ultimate. Also supported are DisplayPort 2.0, PCIe 4.0 and overclocking.
The desktop GPUs are based on the DG2 die, while the laptop GPUs are based on the ACM-G10 die. The DG2 die is available in three different configurations: A380, A580, and A780. The ACM-G10 die is available in four different configurations: the A370M, A550M, A730M, and A770M.
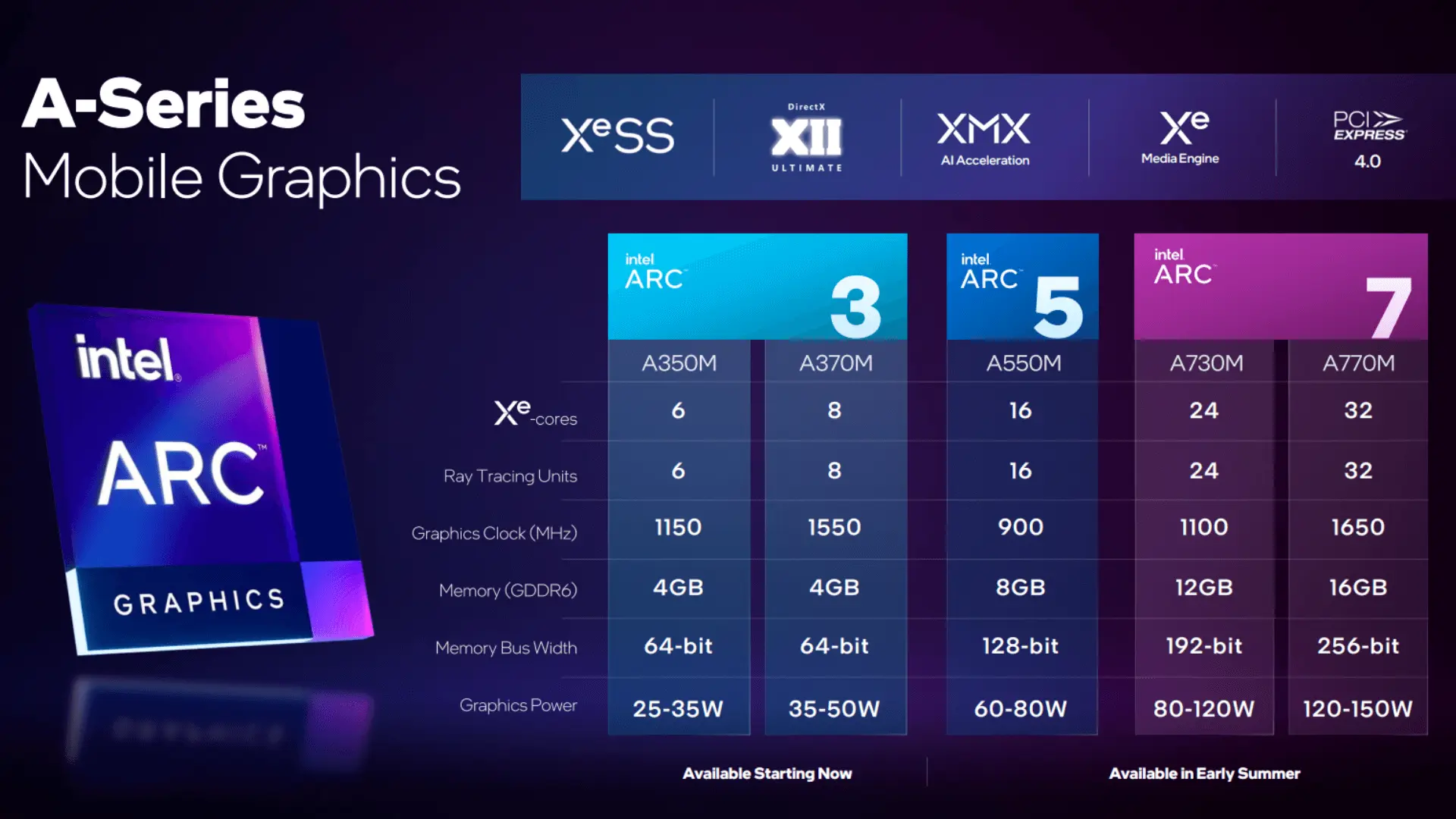
The second generation of Intel Arc GPUs (codenamed “Battlemage”) is expected to be released in 2023. Battlemage will use a new process node from TSMC and is expected to offer significant performance improvements over Alchemist.
According to Intel, these are named after the concept of story arcs found in games. Each generation of Arc is named after each letter of the alphabet in ascending order, beginning with A, then B, then C, and so on. The first generation is named Alchemist, while Battlemage, Celestial and Druid are the respective names for the second, third and fourth Arc generations.
Intel Arc GPUs are a new player in the graphics card market. Intel Arc GPUs are designed to compete with Nvidia’s GeForce RTX and AMD’s Radeon RX GPUs. They offer a good balance of performance and price, and they are a good option for gamers, content creators, and professionals.

Features
Some of the key features of Intel Arc GPUs:
- Hardware-based ray tracing: This allows for more realistic and immersive graphics in games and other applications that support it.
- XeSS: This is a new upscaling technology that can improve the image quality of games without requiring a more powerful GPU.
- DirectX 12 Ultimate: This is the latest version of Microsoft’s graphics API, and it supports a number of features that are used by modern games.
- DisplayPort 2.0: This is the latest version of the DisplayPort standard, and it supports higher resolutions and refresh rates than previous versions. It offers an impressive data transfer rate of 77 Gbits/s.
- Overclocking: This allows users to increase the performance of their GPU by adjusting its clock speed and voltage.
Intel Arc GPUs are a new and exciting addition to the graphics card market. They offer a number of features that are not currently available on other GPUs. If you are looking for a new GPU for gaming or other demanding applications, then Intel Arc GPUs are worth considering.
Hardware-based ray tracing
Hardware-based ray tracing is a new technology that uses dedicated hardware on the graphics card to accelerate ray tracing calculations. This can significantly improve the performance of ray tracing, making it possible to use ray tracing in real-time games and other applications.
Ray tracing is a technique for simulating how light behaves in the real world. It does this by tracing the path of light rays as they interact with objects in a scene. This can be used to create realistic effects such as reflections, shadows, and global illumination.
Traditionally, ray tracing has been a very computationally expensive process. This has limited its use to offline rendering applications, such as video games and movies. However, hardware-based ray tracing can significantly improve the performance of ray tracing, making it possible to use ray tracing in real-time games and other applications.
There are a number of different ways to implement hardware-based ray tracing. One common approach is to use dedicated ray tracing cores on the graphics card. These cores are specifically designed for ray tracing calculations, and they can significantly improve the performance of ray tracing.
Another approach is to use general-purpose compute shaders to implement ray tracing. Compute shaders are a type of shader that can be used to perform general-purpose calculations. They can be used to implement ray tracing, but they are not as efficient as dedicated ray tracing cores.
Hardware-based ray tracing is a promising new technology that has the potential to revolutionize the way we create and experience visual content. By making ray tracing more affordable and accessible, hardware-based ray tracing can enable the creation of more realistic and immersive experiences.

XeSS
Intel XeSS, or Xe Super Sampling, is an upscaling technology that uses artificial intelligence to improve the image quality of games rendered at lower resolutions. It is available on Intel Arc Alchemist graphics cards and can be used to achieve higher frame rates without sacrificing image quality.
XeSS works by first rendering the game at a lower resolution, such as 1080p. The rendered image is then passed to an AI model, which uses machine learning to reconstruct the image at a higher resolution, such as 4K. The reconstructed image is then displayed on the monitor.
XeSS is a more efficient way to achieve higher frame rates than traditional upscaling techniques, such as temporal anti-aliasing (TAA). TAA works by blending multiple frames together to smooth out jagged edges, but it can introduce blur and ghosting artifacts. XeSS, on the other hand, can achieve a similar image quality to TAA without the blur and ghosting artifacts.
XeSS is still under development, but it has already been shown to produce impressive results. In a recent benchmark test, XeSS was able to improve the frame rate of Control by up to 40% while maintaining a similar level of image quality.
Intel XeSS is a promising new technology that has the potential to revolutionize the way we play games. By combining the power of AI with the performance of Intel Arc Alchemist graphics cards, XeSS can deliver stunning visuals at high frame rates.
XeSS is an open-source technology, which means that it can be used by any game developer. This will help to ensure that XeSS support is widely available across a variety of games.
XeSS can be accelerated by the dedicated AI hardware found in Intel Arc Alchemist graphics cards. This will help to improve the performance of XeSS, especially on high-resolution displays.
XeSS can be used to improve the image quality of games rendered at a variety of resolutions. This means that XeSS can be used to improve the performance of games on both high-end and low-end hardware.
Overall, Intel XeSS is a powerful new technology that has the potential to revolutionize the way we play games. By combining the power of AI with the performance of Intel Arc Alchemist graphics cards, XeSS can deliver stunning visuals at high frame rates.

DirectX 12 Ultimate
DirectX 12 Ultimate is the latest version of the DirectX API, and it is designed to enable the next generation of games and graphics applications. It builds on the foundation of DirectX 12, and it adds new features that can improve performance, visual fidelity, and immersion.
Some of the key features of DirectX 12 Ultimate include:
- Ray tracing: Ray tracing is a new technology that allows games to simulate how light behaves in the real world. This can be used to create realistic effects such as reflections, shadows, and global illumination.
- Variable rate shading: Variable rate shading is a new technique that allows different parts of a scene to be rendered at different levels of detail. This can improve performance without sacrificing image quality.
- Mesh shaders: Mesh shaders are a new type of shader that allows developers to create more complex and detailed models.
- Sampler feedback: Sampler feedback is a new feature that allows developers to gather information about how textures are being used in a scene. This information can be used to improve performance and visual quality.
DirectX 12 Ultimate is supported by a wide range of hardware, including the latest graphics cards from AMD, NVIDIA, and Intel. It is also supported by a growing number of games and graphics applications.
If you are looking to experience the best possible graphics and performance in games and graphics applications, then you should consider using DirectX 12 Ultimate.
Here are some of the benefits of using DirectX 12 Ultimate:
- Realistic graphics: Ray tracing can create realistic effects such as reflections, shadows, and global illumination. This can make games look more immersive and realistic.
- Improved performance: Variable rate shading can improve performance without sacrificing image quality. This can make games run smoother and with less stuttering.
- More detailed models: Mesh shaders can be used to create more detailed and complex models. This can make games look more realistic and immersive.
- Improved performance and quality: Sampler feedback can be used to improve performance and visual quality. This can make games run smoother and look better.
If you are looking for the best possible gaming experience, then you should consider using DirectX 12 Ultimate.
DisplayPort 2.0
DisplayPort 2.0 is the latest version of the DisplayPort standard, and it offers several significant improvements over the previous version. These improvements include:
- Higher bandwidth: DisplayPort 2.0 has a bandwidth of 77.37 Gbps, which is three times the bandwidth of DisplayPort 1.4. This increased bandwidth allows for higher resolutions, higher refresh rates, and better HDR support.
- Support for 16K resolution: DisplayPort 2.0 can support resolutions up to 16K (15360 × 8640) at 60 Hz. This is four times the resolution of 4K.
- Support for HDR10+: DisplayPort 2.0 supports the HDR10+ dynamic metadata format. This format allows for more accurate and realistic HDR images.
- Support for Multi-Stream Transport (MST): DisplayPort 2.0 supports MST, which allows you to daisy chain multiple displays from a single DisplayPort output.
- Support for USB 2.0 data transfer: DisplayPort 2.0 can also be used to transfer USB 2.0 data, which allows you to connect peripherals such as keyboards and mice to your display.
DisplayPort 2.0 is a significant improvement over the previous version of the standard, and it offers several features that are sure to be appealing to gamers, content creators, and other users who demand high-quality visuals.
Overclocking
Overclocking is the process of increasing the clock speed of a processor or graphics card beyond its stock settings. This can be done to improve performance, but it can also increase the risk of instability and damage.
Intel Arc GPUs support overclocking through the Arc Control software. To overclock your Arc GPU, follow these steps:
- Open Arc Control.
- Click on the “Performance” tab.
- Under “Overclocking,” click on the “Advanced” button.
- In the “GPU Performance Boost” section, drag the slider to increase the clock speed.
- Click on the “Save” button.
It is important to note that overclocking can increase the temperature and power consumption of your GPU. If you experience any instability or performance issues, you may need to reduce the clock speed.
Here are some tips for overclocking your Arc GPU:
- Start with a small increase in clock speed and test for stability.
- Increase the clock speed in small increments until you reach the desired performance.
- Monitor the temperature and power consumption of your GPU to make sure they do not exceed safe limits.
- Be aware that overclocking can void the warranty on your GPU.
Overclocking can be a great way to improve the performance of your Arc GPU. However, it is important to do so safely and responsibly. By following these tips, you can safely overclock your Arc GPU and enjoy improved performance.
Here are some of the benefits of overclocking your Arc GPU:
- Increased performance: Overclocking can improve the performance of your Arc GPU by up to 10%. This can be especially beneficial for gaming and other demanding applications.
- Reduced latency: Overclocking can also reduce the latency of your Arc GPU, which can improve the overall responsiveness of your system.
- Increased stability: Overclocking can sometimes make your Arc GPU more stable, especially if you are experiencing issues with crashes or stuttering.
However, there are also some risks associated with overclocking your Arc GPU:
- Increased heat: Overclocking can increase the heat output of your Arc GPU, which can lead to overheating and performance throttling.
- Reduced lifespan: Overclocking can also reduce the lifespan of your Arc GPU, as it will be under more stress.
- Instability: Overclocking can sometimes make your Arc GPU unstable, which can lead to crashes or other issues.
Overall, overclocking can be a good way to improve the performance of your Arc GPU. However, it is important to weigh the risks and benefits before doing so. If you are not comfortable overclocking, you should not do it.
Intel Xe HPG
Intel Xe HPG is the high-performance graphics variant of the Xe architecture. It is designed for gamers and creators who demand the best possible performance and features. Xe HPG features a new microarchitecture that is optimized for both rasterization and ray tracing. It also supports the latest APIs, including DirectX 12 Ultimate and Vulkan. It is a New microarchitecture that is optimized for both rasterization and ray tracing Support for the latest APIs, including DirectX 12 Ultimate and Vulkan.
Intel XMX
Intel XMX is a set of new instructions that are designed to accelerate matrix multiplication operations. These instructions are available on Intel’s latest generation of Xe-HPG GPUs, which are designed for high-performance gaming and compute workloads.
XMX instructions can provide significant performance improvements for a variety of matrix multiplication-based workloads, including Deep learning inference, Computer vision, Natural language processing, Financial modeling, Scientific computing
XMX instructions are available on all Intel Xe-HPG GPUs, including the Arc A770M, Arc A750M, and Arc A550M. These GPUs are available in a variety of laptop and desktop configurations.
To take advantage of XMX instructions, developers will need to use a compiler that supports them. Intel’s oneAPI DPC++ compiler is one such compiler.
XMX instructions are a powerful new addition to the Intel Xe-HPG architecture. They can provide significant performance improvements for a variety of matrix multiplication-based workloads.

Intel Deep Link
Intel Deep Link is a technology that allows Intel CPUs and GPUs to work together to improve performance and efficiency. It does this by dynamically allocating power between the CPU and GPU, depending on the needs of the workload. This can result in significant performance boosts for tasks such as gaming, video editing, and AI processing.
Intel Deep Link is supported on select Intel Core processors and Intel Arc graphics cards. Intel Deep Link is a powerful tool that can help you get the most out of your Intel hardware.
PCIe 4
PCIe 4 (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express 4) is the fourth generation of the PCIe standard, which is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard designed to replace the older PCI bus standard. It is the common motherboard interface for personal computers’ graphics cards, sound cards, hard disk drive host adapters, solid-state drives, Wi-Fi and Ethernet hardware connections.
PCIe 4 doubles the data rate of PCIe 3, allowing PCIe 4 devices to transfer data at much faster speeds. PCIe 3 operates at 8 GT/s (gigatransfers per second) which roughly translates to 1 GB/s per PCIe lane. By comparison, PCIe 4 operates at 16 GT/s, or around 2 GB/s (gigabytes per second) per PCIe lane.
GDDR6 Memory
GDDR6 (Graphics Double Data Rate 6) is the sixth generation of GDDR SDRAM, a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory with a high bandwidth, “double data rate” interface, designed for use in graphics cards, game consoles, and high-performance computing. It is the successor to GDDR5 and was first released in 2017.
GDDR6 offers a number of improvements over GDDR5, including:
- Increased clock speed: GDDR6 operates at a clock speed of up to 16 Gbps, which is twice as fast as GDDR5.
- Increased memory bandwidth: GDDR6 has a memory bandwidth of up to 64 GB/s, which is twice as much as GDDR5.
- Lower power consumption: GDDR6 consumes less power than GDDR5, which can help to improve the overall performance of a graphics card.
GDDR6 is used in a wide variety of graphics cards, including high-end gaming cards, professional cards, and integrated graphics solutions. It is also used in some game consoles, such as the Xbox Series X and the PlayStation 5.
Performance
Intel Arc A770 Vs Intel Arc A750 Vs Nvidia GeForce RTX 3060 VS AMD RX 6600 XT
We are going to compare Intel’s Arc A770 and Intel’s Arc A750 performance against Nvidia’s GeForce RTX 3060 and AMD’s RX 6600 XT. First let us look at the specifications of individual GPUs…
| Intel Arc Alchemist A770 | Intel Arc Alchemist A750 | Nvidia GeForce RTX 3060 | AMD RX 6600 XT | |
| Cores | 512 Xe-Cores | 448 Xe-Cores | 3584 CUDA Cores | 2048 Stream Cores |
| Ray Tracing cores | 32 | 28 | 28 | Nil |
| Base Clock Speed | 1905 MHz | 1800 MHz | 1320 MHz | 2350 MHz |
| Boost Clock Speed | 2450 MHz | 2300 MHz | 1785 MHz | 2359 MHz |
| Memory | 16 GB GDDR6 | 8 GB GDDR6 | 12 GB GDDR6 | 8 GB GDDR6 |
| Memory Bus | 256-bit | 256-bit | 192-bit | 128-bit |
| Bandwidth | 560 GB/s | 512 GB/s | 360 GB/s | 256 GB/s |
| TDP | 250W | 225 W | 170 W | 160 W |
| Price | $350 (~ ₹28,700) | $250 (~ ₹20,500) | $340 (~ ₹27,900) | $380 (~ ₹31,200) |
CUDA cores and Xe cores are both types of processing units found in graphics processing units (GPUs). CUDA cores are Nvidia’s proprietary technology, while Xe cores are Intel’s. Both types of cores are designed for parallel processing, which means they can perform multiple tasks at the same time. This makes them well-suited for tasks such as video editing, 3D rendering, and machine learning.
The latest generation of Xe cores, codenamed Alchemist, is said to be on par with or even faster than CUDA cores in some cases.
Another difference between CUDA cores and Xe cores is their programming model. CUDA cores use the CUDA programming language, while Xe cores use the OpenCL programming language. Both languages are open source, but CUDA is more widely used. This means that there is a larger library of CUDA-based applications available than there are OpenCL-based applications.
You may see a large number of core differences. But the Benchmarks would amaze you. Arc GPU has better Specs in all other aspects except core count.
OpenCL Benchmarks
| GPU | Score |
| Intel Arc A770 | 99,488 |
| Nvidia RTX 3060 | 96,430 |
| Intel Arc A750 | 88,834 |
| AMD RX 6600 XT | 82,634 |
Intel Arc A770 dominates as it has native OpenCL Support. Nvidia RTX 3060 falls behind by 3000 scores. Intel Arc A750 and AMD RX 6600 XT fall each 6000 scores behind.
Vulkan Benchmarks
| GPU | Score |
| Nvidia RTX 3060 | 74,412 |
| Intel Arc A770 | 73,558 |
| Intel Arc A750 | 66,639 |
| AMD RX 6600 XT | 64,563 |
Nvidia RTX 3060 takes a slight edge of around 900 scores ahead of Intel Arc A770 in Vulkan Engine. Then falls Intel A750 and AMD RX 6600 XT.
Gaming Performance
Here are the benchmarks of Red Dead Redemption 2 with various cards.
| GPU | FPS |
| AMD RX 6600 XT | 94 FPS |
| Intel Arc A770 | 87 FPS |
| Intel Arc A750 | 80 FPS |
| Nvidia RTX 3060 | 78 FPS |
| GPU | FPS |
| Intel Arc A770 | 69 FPS |
| AMD RX 6600 XT | 65 FPS |
| Intel Arc A750 | 62 FPS |
| Nvidia RTX 3060 | 60 FPS |
| GPU | FPS |
| Intel Arc A770 | 46 FPS |
| Nvidia RTX 3060 | 39 FPS |
| Intel Arc A750 | 33 FPS |
| AMD RX 6600 XT | 29 FPS |
You could see that Intel A770 has dominated the gaming benchmarks. Intel A750 and Nvidia RTX 3060 is on par with each other. RX 6600 XT lacks Ray tracing, which puts it behind the competitors.
Final Verdict
Intel’s Arc GPUs have been met with mixed reviews. Some reviewers have praised the performance of the Arc A770, while others have criticized the lack of availability and price.
It is important to note that the Arc GPU is still a new product, and its drivers are not yet fully optimized.
As you can see, the Intel Arc A770 is generally able to match or exceed the performance of the Nvidia RTX 3060 and AMD Radeon RX 6600 XT. However, it is important to note that these benchmarks were conducted using early drivers, and the performance of the Arc A770 may improve in the future.
Overall, it is too early to say whether Intel’s Arc GPUs will be a success. However, the company has made a good start and is likely to continue to improve the performance and availability of its GPUs in the future.
I hope this article would be the best one which you could find on the internet. It took days to make this article, so please consider sharing our article on social media and make the world know about our blog. Thanks for your Interest and Support.
Buy Now
Read More about Intel’s Arc GPUs @ Intel® Arc™ Graphics Overview


